Discovering Vernacular Architecture: Celebrating Australia’s Rich Heritage and Unique Identity
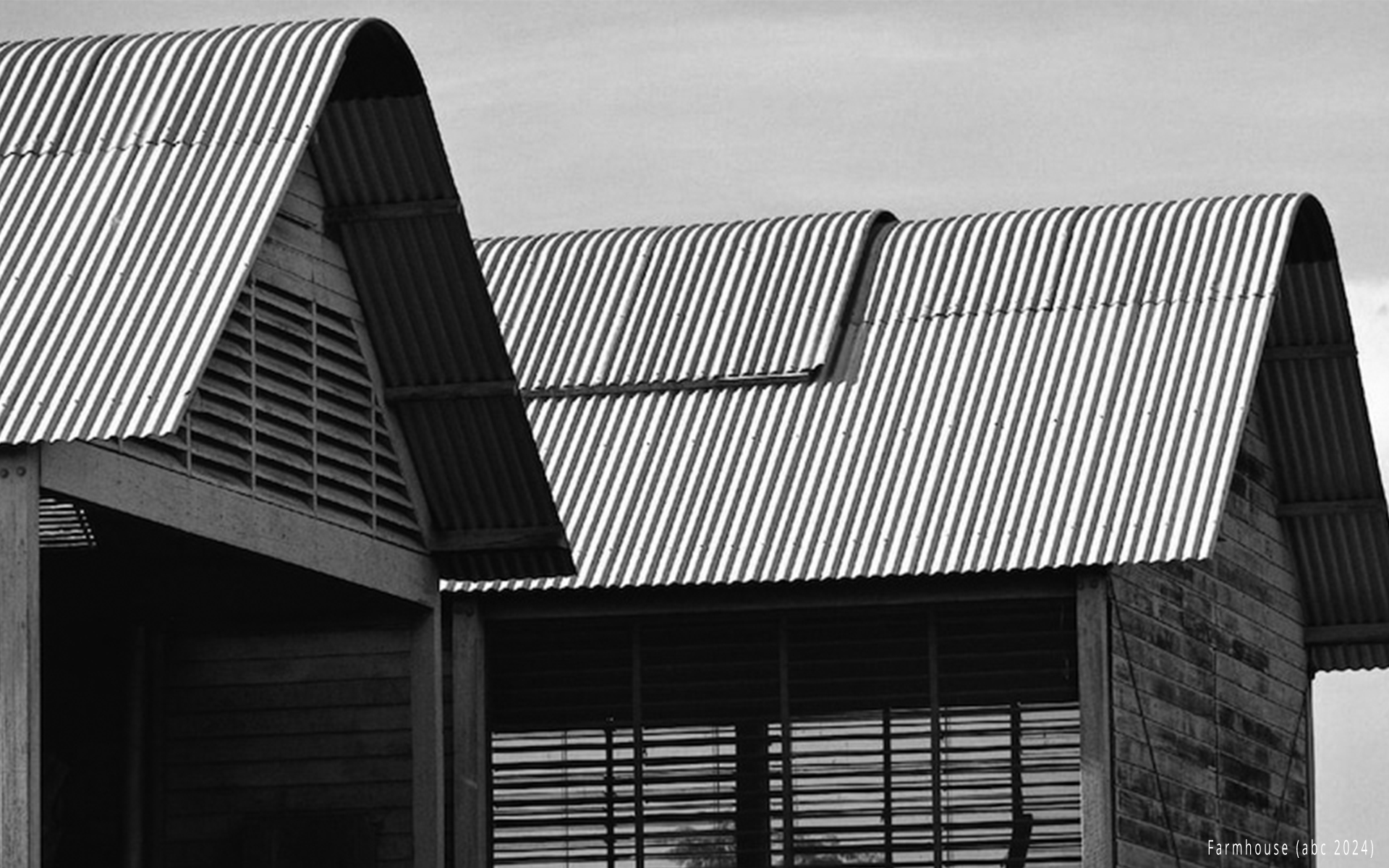
Australia’s diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage have given rise to a remarkable architectural style known as Vernacular architecture. Rooted in tradition and influenced by the environment, Vernacular architecture reflects the unique identity of different regions across the country. In this article, we embark on a journey through Australia’s vernacular architecture, exploring its origins, defining features, and enduring significance in contemporary design.
Understanding Vernacular Architecture:
Vernacular architecture is an indigenous architectural style that evolves over time through a deep understanding of local climate, materials, and cultural traditions. It embodies the wisdom and craftsmanship of generations, responding to the needs of the community and harmonizing with the surrounding landscape.
Origins and Regional Influences:
Australia’s vastness and geographical diversity have given rise to various regional vernacular styles, each shaped by climate, available resources, and cultural influences. From the tropical north to the temperate south, and from coastal regions to the arid inland, each area showcases distinct architectural expressions.
The Tropical North: Indigenous communities in northern Australia embraced the use of lightweight materials and elevated structures to cope with the tropical climate, promoting natural ventilation and protection from floods.
The Coastal Regions: Traditional beachside dwellings in coastal areas often feature timber construction, expansive verandas, and flexible layouts to capture coastal breezes and embrace outdoor living.
The Arid Inland: In the arid outback, structures were built using local materials such as mudbrick or stone, with thick walls providing insulation against extreme temperatures.
Defining Features of Vernacular Architecture:
Climate-Responsive Design: Vernacular buildings are meticulously designed to respond to the unique climatic conditions of their region. Passive design principles, such as orientation, shading, and ventilation, play a central role in ensuring comfort and energy efficiency.
Use of Local Materials: Vernacular architecture relies on locally available materials, celebrating the beauty and resilience of natural resources. From timber and stone to mud and thatch, these materials anchor the structures to their environment.
Sustainable Practices: Emphasizing sustainability, Vernacular architecture minimizes the environmental impact of construction by utilizing renewable resources and embracing adaptive reuse.
Cultural Significance: Beyond functional aspects, Vernacular architecture holds immense cultural value, preserving the stories, traditions, and identity of local communities.
Vernacular Architecture in Contemporary Design:
In the modern context, architects draw inspiration from the principles of Vernacular architecture to create sustainable and contextually relevant designs. The revival of traditional construction techniques, coupled with innovative technologies, allows for the integration of timeless wisdom with contemporary sensibilities.
Preserving Heritage and Embracing the Future:
Preserving Vernacular architecture is crucial in maintaining Australia’s cultural heritage and fostering a sense of place and belonging. By recognizing and embracing these design principles, architects can create spaces that not only reflect Australia’s unique identity but also nurture a deeper connection with the land and its people.
Australia’s Vernacular architecture stands as a testament to the harmonious relationship between humans and their environment. Rooted in tradition, this indigenous architectural style continues to inspire contemporary design, reminding us of the importance of sustainable practices, cultural preservation, and a profound respect for the land we call home. As we celebrate Australia’s rich heritage, let us embrace the spirit of Vernacular architecture to shape a more sustainable and culturally enriched future.